Kamostat
Kamostat veya camostat bir serin proteaz inhibitörüdür. Serin proteaz enzimleri vücutta çeşitli fonksiyonlara sahiptir ve bu nedenle kamostatın çeşitli kullanım alanları vardır. Camostat Japonya'da kronik pankreatit ve postoperatif reflü özofajit tedavisi için onaylanmıştır.[1] Ono Pharmaceutical, Camostat'ın üreticisidir. İlaç aynı zamanda bazı kanser türlerinin tedavisinde kullanılır ve bazı viral enfeksiyonlara karşı etkilidir. Madde karaciğer, böbrek hastalığı veya pankreatitte fibrozu inhibe edebilir.[2][3][4][5][6]
| Kamostat | |
|---|---|
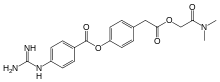 | |
| Sistematik (IUPAC) adı | |
| N,N-Dimethylcarbamoylmethyl 4-(4-guanidinobenzoyloxy)phenylacetate | |
| Kimyasal özellikler | |
| SMILES | search in eMolecules, PubChem |
| Tedavi bilgileri | |
| Yasal durum | ?(ABD) ℞ Prescription only |
Kamostat, transmembran proteaz, serin 2 (TMPRSS2) enziminin bir inhibitörüdür. HeLa hücrelerinde TMPRSS2'nin inhibe edilmesi, SARS-CoV ve insan koronavirüsü NL63 enfeksiyonlarının kısmen bloke edilmesine yol açmaktadır.[7] Başka bir in vitro çalışma, Camostat'ın Calu-3 akciğer hücrelerinin COVID-19'dan sorumlu virüs SARS-CoV-2 tarafından enfekte edilmesini önemli ölçüde azalttığını göstermektedir.[8]
Camostat, kronik pankreatit için tipik olarak günde 600 mg, postoperatif reflü özofajit için ise 300 mg alınır. Günlük miktar 3 doza bölünür ve yemekten sonra alınır.[9]
Kaynakça
- "Camostat". drugs.com. 5 Mart 2020 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 22 Mart 2020.
- Okuno, M.; Kojima, S.; Akita, K.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Adachi, S.; Sano, T.; Takano, Y.; Takai, K.; Obora, A.; Yasuda, I.; Shiratori, Y.; Okano, Y.; Shimada, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Muto, Y.; Moriwaki, Y. (2002). "Retinoids in liver fibrosis and cancer". Frontiers in Bioscience. 7 (4). ss. d204-18. doi:10.2741/A775. PMID 11779708.
- Hsieh, H. P.; Hsu, J. T. (2007). "Strategies of development of antiviral agents directed against influenza virus replication". Current Pharmaceutical Design. 13 (34). ss. 3531-42. doi:10.2174/138161207782794248. PMID 18220789.
- Kitamura, K.; Tomita, K. (2012). "Proteolytic activation of the epithelial sodium channel and therapeutic application of a serine protease inhibitor for the treatment of salt-sensitive hypertension". Clinical and Experimental Nephrology. 16 (1). ss. 44-8. doi:10.1007/s10157-011-0506-1. PMID 22038264.
- Zhou, Y.; Vedantham, P.; Lu, K.; Agudelo, J.; Carrion Jr, R.; Nunneley, J. W.; Barnard, D.; Pöhlmann, S.; McKerrow, J. H.; Renslo, A. R.; Simmons, G. (2015). "Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry". Antiviral Research. Cilt 116. ss. 76-84. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.01.011. PMC 4774534 $2. PMID 25666761.
- Ueda, M.; Uchimura, K.; Narita, Y.; Miyasato, Y.; Mizumoto, T.; Morinaga, J.; Hayata, M.; Kakizoe, Y.; Adachi, M.; Miyoshi, T.; Shiraishi, N.; Kadowaki, D.; Sakai, Y.; Mukoyama, M.; Kitamura, K. (2015). "The serine protease inhibitor camostat mesilate attenuates the progression of chronic kidney disease through its antioxidant effects". Nephron. 129 (3). ss. 223-32. doi:10.1159/000375308. PMID 25766432.
- Kawase M, Shirato K, van der Hoek L, Taguchi F, Matsuyama S (Haziran 2012). "Simultaneous treatment of human bronchial epithelial cells with serine and cysteine protease inhibitors prevents severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus entry". J. Virol. 86 (12). ss. 6537-45. doi:10.1128/JVI.00094-12. PMC 3393535 $2. PMID 22496216.
- Hoffman, Markus (5 Mart 2020). "SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor". Cell. 14 Mart 2020 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 5 Mart 2020.
- http://www.shijiebiaopin.net/upload/product/201272318373223.PDF
Dış bağlantılar
- Kunze H, Bohn E (Mayıs 1983). "Effects of the serine protease inhibitors FOY and FOY 305 on phospholipase A1 (EC 3.1.1.32) activity in rat - liver lysosomes". Pharmacol Res Commun. 15 (5). ss. 451-9. doi:10.1016/S0031-6989(83)80065-4. PMID 6412250.
- Göke B, Stöckmann F, Müller R, Lankisch PG, Creutzfeldt W (1984). "Effect of a specific serine protease inhibitor on the rat pancreas: systemic administration of camostate and exocrine pancreatic secretion". Digestion. 30 (3). ss. 171-8. doi:10.1159/000199102. PMID 6209186.